As you all know the first thing that we all do after getting our hands on the IP address is scan and the first tool that comes to mind is Nmap. A great and awesome tool but there is the main problem with this tool it’s tooooooo slow.
A full port scan take can up to 20–30 minutes, and after Nmap then comes the Masscan, a fast tool that can scan any target so easily and can be so fast. We have seen people, starting with a Masscan and then using that result for a Nmap scan but still, you have to do the manual work of starting a Nmap. That’s where RustScan is so useful.

|
| RustScan scan (Full port scan) — 39 seconds |
It's a lifesaver, most of us hate waiting for Nmap output results but this
tool is a beast. However, apart from the long waiting time for output. Nmap is
better than every tool out there for the port scan.
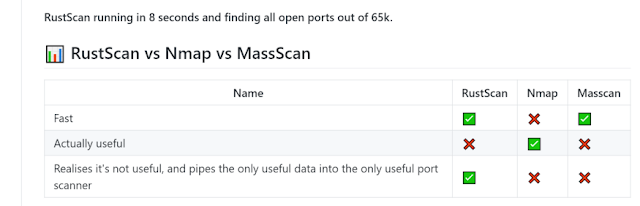
|
| A comparison by the author of the tool |
Installation Guide
Nmap is Required. If you do not have Nmap installed, follow the installation guide. RustScan has many possibilities and options to choose
from. It can be installed on
Docker, Kali Linux/Debian
machines, and many more. Follow the installation guide of RustScan to install on the platform of your choice.
Usage
rustscan -a <IP>
Normally after rustscan finishes the scan, it starts a Nmap scan against the
target by specifying the flag -vvv (maximum verbosity) by default.
RustScan is faster, why?
- Low-level kernel networking.
- Written in a fast language (Rust)
- Asynchronous scanning.
RustScan conducts a preliminary scan using its own internal discovery
technique: it creates sockets against its targets and waits for their
responses. In nutshell, RustScan uses a full
TCP 3-way handshake
connection via the built-in Rust sockets module.
Once this first scanning stage is completed it executes Nmap with the specific
flags, by default, which aims to discover the targets’ operating systems.
We hope this helps. If any suggestions or doubts you can add a comment and we
will reply as soon as possible.



%20Cover.jpg)

%20Cover.jpg)


No comments:
Post a Comment