
Nmap is the most used port scanning tool on the Internet and it is reasonable
too as it is extremely powerful. With these Nmap basic commands, you can
gather information on a target by running port scanning and
fingerprinting.
The basic and default SYN scan will scan 1000 TCP ports on the target specified.
- Syntax: nmap <IP>
- Example: nmap 192.168.0.105
If a non-root user adds sudo, in the beginning, sudo nmap <IP>
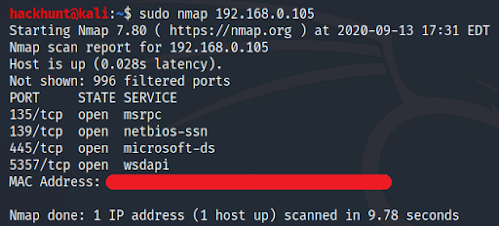
If you run the Nmap with root access, Nmap will do a so-called privileged scan
which is a RAW SYN Stealth Scan. But if you run Nmap as a non-root
access, it will do a so-called unprivileged scan which is
TCP Connect Scan
which is apparently slower and can be detectable.
So, with the root privileges, the Nmap is able to send an SYN packet
and then SYN-ACK that comes back is enough to know if there is an
actual open port.
But, with the non-root privileges, the Nmap cannot send
Raw TCP/IP packets. So, it has to call the
Operating System to do a full connect which makes it slower and
more probable to get recorded in system logs as it does a full
TCP Connect to obtain the port information.
Not sure about SYN or SYN-ACK or TCP Connect?
All in all, with root access it is an SYN Scan, without root it is a full connect scan.
We hope this helps. If any suggestions or doubts you can add a comment and
we will reply as soon as possible.

%20Cover.jpg)
%20Cover.jpg)



No comments:
Post a Comment