Foremost is a forensic data recovery integrated tool for Linux used to
recover files using their headers, footers, and data structures through a
process known as file carving. Although it was developed for law enforcement
use, however, it is freely available. It can be used as a general data
recovery tool. Foremost can slice FATx, NTFS, ext2/3, or raw partition files
independently of the file system. It is helpful for both researching digital
forensics and for the retrieval of files.
Before getting into the tool, you have to first insert the disk from which you
want to carve or recover the data, you can also recover the files from disk
drives. For the sake of the explanation, we are using a SanDisk 8 GigaBit USB
Flash Drive.
-
First, to check whether the USB drive is actually inserted properly or not;
we can use the command
sudo fdisk -l.

|
|
Checking the Disk Location
|
It shows under the substantial path which is
/dev/sdb1 with 7.5G of size means the USB is inserted successfully.
-
Now, to install Foremost utility, using Kali Linux terminal; type
sudo apt install foremost -y.

|
|
Installing Foremost
|
-
We have to make the output directory where the recovered file should be
stored. In this scenario, we are making a directory CFB on the Desktop using
the command
mkdir.

|
| Output Directory |
- You can use the help command for a better understanding of the tool.
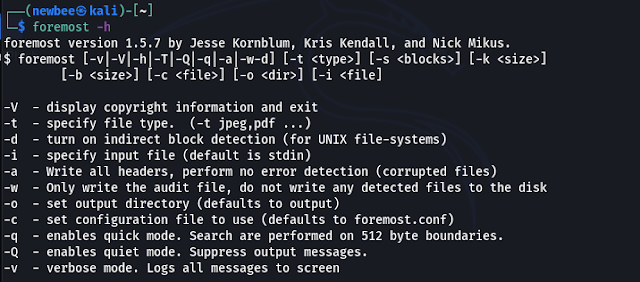
|
|
Help Command of Foremost
|
Take your time and go through all the options in the tool. Here we will
discuss some basic commands.
-
The scenario here is to recover the images (JPEG) from the USB
(/dev/sdb1).
-
The flags we will be using are -i, -a, -t,
-T.
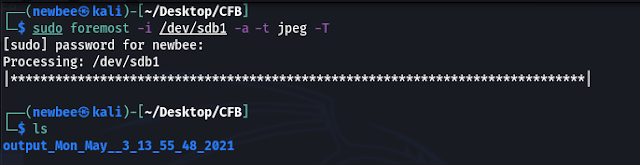
|
| Recovery process |
-
A new directory is created, cd to that directory and you will
also, data was recovered.

|
|
Recovered Files
|
You can specify any file extension and
recover the data.
We hope this helps. If any suggestions or doubts you can add a comment and
we will reply as soon as possible.








%20Cover.jpg)

%20Cover.jpg)


No comments:
Post a Comment